Business plan for UNIDO standards
Business plans are developed for different businesses and for different purposes. In this case, the presentation of the business plan can be in any order. Nevertheless, some standards have been adopted in the world, according to which it is better to structure their data and calculations.
The most popular standard for compiling business plans is the UNIDO (United Nations Industrial Development Organization) standard. Its peculiarity is that the structure offered by this standard is suitable for most types of business. The business plan, compiled according to the structure of the UNIDO standard, is suitable for private use, for working with an investor or a partner. Yakist’s specialists are also advised to use this standard when developing business plans for obtaining a loan, filing documents with the bank or in a fund to receive a grant.
According to UNIDO standards, the structure of the business plan should consist of the following items:
- Summary
- Description of the business idea
- Description of goods or services
- Review of the analysis of competitors
- Analysis of the target market
- Marketing plan
- Production plan
- Organizational plan
- Financial plan
- Project Effectiveness Evaluation
- Risk analysis
- Annexes
Usually, the biggest questions come to the description account, which should be in Summary. Summaries are short excerpts from a business plan. Since this is the very first thing that investors and creditors look through, it is best to submit information that will be interesting to them. Therefore, in the Summary it is recommended to reduce the description of goods and services, and focus on information with numbers. Simply give answers to the questions of interest to the investor:
– what is the volume of investments and their distribution;
– terms and conditions of lending;
– volume of own funds;
– project development schedule;
– project performance indicators;
– payback schedule and calculation of the break-even point of the project.
The remaining parts of the business plan should give more extended information on each component. It is important that the information in the following paragraphs proves the correctness of the calculations and confirms the development trends of the project.
Description of the business idea
The description of the business idea should give a clear understanding of the investor about the need, vitality and profitability of your idea. In order to persuade the investor to describe the concept of business, indicating their advantages and differences from competitors. Concentrate on important aspects following this plan:
- Uniqueness of the business idea
- Viability of the business idea
- Feasibility of a business idea
- The urgency of the business idea
- Relevance of your skills and experience level
The business plan, compiled according to the UNIDO standards, is very logical and assumes that if the investor is interested in your idea, he will further want to study the characteristics of the goods or the essence of the services in more detail.
Description of goods and services
In this part of the business plan, you need to provide a description of the product or service of the business. In the description it is important to show not only the main characteristics of your product or service, but also to emphasize the need for your product.
If your product or service is related to a start-up, you can still describe the impact of your offer on the existing market.
Review of the analysis of competitors
Performing the analysis of competitors, make a profile of the competitor. Indicate the level of maturity, the years of existence in the target market, the corporate size, whether there is a deductible and much more. After that, evaluate the competitive position. Next, go to a review of the prices of competitors. An important factor in the analysis of competitors can be and analysis of product delivery, packaging. The review of the analysis of competitors is best completed with conclusions indicating the existing strategic opportunities.
In this part of the business plan, it is recommended to assess your own strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors. In other words, this is called a SWOT analysis.
Target Market Analysis
The analysis of the target market or market is the basis of your further calculations and marketing plan. In the analysis of the target market, it is important to give not only a general idea of those who can benefit from your product or service, but also create an avatar of the client. To do this, conduct a survey or gather an analyst about potential potential buyers.
Then clearly describe the client. Specify its age, sex, income level, education, demographic (ethnic or national segments), location (country / city, visitors of the facility, city residents, transit passengers), seasonal (summer tourists, holidaymakers), others.
Moving further on the structure of the business plan for UNIDO standards go to the marketing plan.
Marketing plan
Previous market analysis results will convince the investor that the market for your product or service exists. In the marketing plan, you need to display how you will attract your customers.
To date, the choice of marketing strategy takes a key place in the implementation of business ideas. Careful study of the scheme of sales of goods, packaging and delivery, after-sales service are all important components of the marketing plan. Do not think that the price of the goods should be attributed only to the costs of attracting customers. Also, it is necessary to take into account the additional costs that will be associated with marketing. For example, there may be additional costs associated with repairing the product or returning.
Effective marketing strategy begins with the company’s philosophy and mission, which determine the vector of product development.
Production plan
This section of the business plan is described only by entrepreneurs who are engaged in production. The production plan can consist of a description and diagrams on which the technology of production is displayed. Qualitative study of the production plan will allow to track the entire production cycle. Thus, you can answer the following questions:
- Production location. Required area and composition of buildings and premises;
- Analysis of access roads;
- Availability of necessary communications;
- List of equipment and analysis of capacities for production. How much time does the equipment supply, if there are specialists in setting up and repairing equipment;
- Conditions for the purchase of raw materials for production. List of main suppliers, prices and terms of delivery;
- State support, benefits, legal regulation (the existence of special conditions, the need for licensing).
The production plan is developed with a perspective of 3-5 years. Making a forecast of expanding the business and increasing production, you need to know the maximum production volumes that are possible for the equipment. With the increase in production, the amount of power consumed is also increased, that is, current and constant costs will increase.
Therefore, making assumptions in the production plan, it is best to consult with specialists in this field.
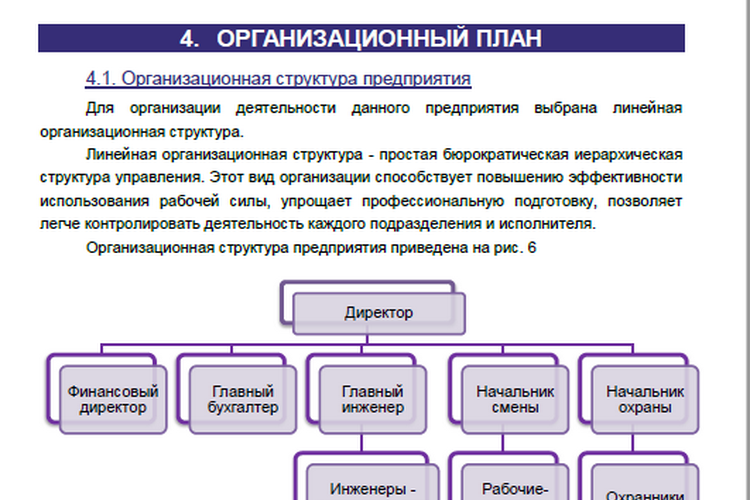
Organizational plan
The success of the project is determined by the management team and the correct organization of work in the business project.
The organizational structure of the enterprise will indicate the need for each employee. A brief description of the job description of employees will give an idea of its downloading and qualification.
In addition, it is important to give information about partners and company management.
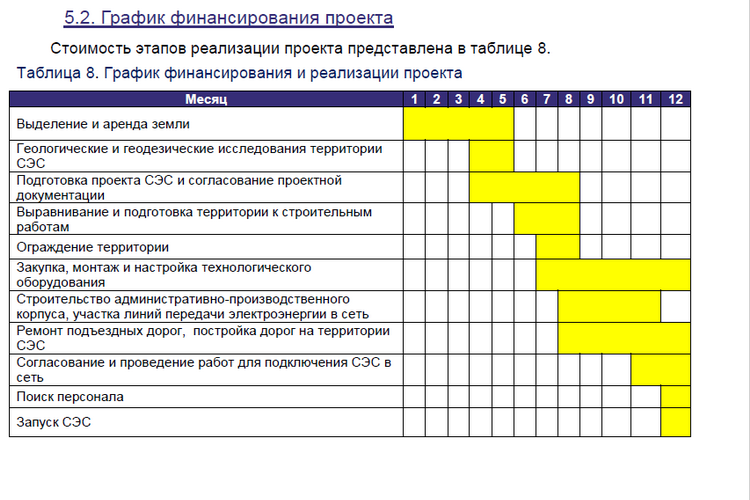
The organizational plan should include a project implementation plan. It is best to provide a graphic material indicating where your project is at the moment and how long it will take to complete it.
Financial plan
To logically build a financial plan writing, we recommend that you follow this algorithm:
- Describe the amount of investment you need. Indicate the distribution of investment funds.
- Calculate the costs of the preparatory period;
- Calculate the cost of the main period, indicating the cost of production or service;
- Calculate future sales revenue;
- If there is a loan, indicate the repayment schedule for the principal amount and payment of interest on the loan;
- Indicate the amount of taxes that the company will pay for the time of work (according to the forecast);
- Write a profit and loss account;
- Write a statement of cash flows;
- Balance the forecast balance of the project.
Project Effectiveness Evaluation
The concept of project efficiency and methods of definition are quite diverse. The effectiveness of the project is the evaluation of the results. There are a number of key project indicators that will influence the decision of the investor.
These indicators: net cash flow, the calculation of the break-even point, the payback period. And also the value of NPV, IRR, return on investment and others.
Risk analysis
This paragraph gives a brief description of the possible risks, ways to minimize them, and possible force majeure.
Apps
All information collected during the writing of the business plan for the UNIDO standard is appended as Add-ons. Main Applications can be: preliminary contracts for the supply or purchase, commercial offers, schemes, drawings and other important information.
Short summary
Drawing up a business plan for the UNIDO standard helps to streamline the data on the implementation of the idea. Based on this business plan it is easy to make a presentation of the project. Avoid excessive description and praise of your strengths. Submit information briefly and reasonably.
A competently drawn up business plan is not a formal necessity, but a functional guide in the business world