Create a business model. The secret is 9 blocks.
We continue the series of articles on planning.
Who else is not with us, we remind that 52 steps to planning (#52_bsteps) is a series of articles that will help organize information, prioritize, develop a strategy, create a work plan and move in the right direction.
So, today we will talk about the development of the business model of the organization.
The very concept of the business model leads us to the fact that it becomes clear its essence – business modeling. If you understand literally, the simulation came to us from the French language from the word “modele” – a sample, a prototype, and business from English “business” and means “business”, “occupation”, “enterprise”. Therefore, the business model is a sample of the enterprise.
The origins of business modeling
The concept of a business model is quite new, for the first time it was sounded in the annotations to scientific works on economic topics in the late 1940s. The development of business-modeling has already developed with the development of the Internet.
And only in 2004, Alexander Osterwalder, the business model was presented schematically, in the form of a blueprint for which the company operates. Practical examples and general availability to the outline of the business model, he developed in the book “ Business Model Generation.”
The secret of nine blocks
According to Osterwalder, the work of any company can be described using 9 blocks. These blocks describe the scheme of work, the main processes and resources.
So, these are the structural blocks:
- Consumer segments
- Value propositions
- Distribution channels
- Relationships with customers
- Income revenue streams
- Key resources
- Key Activities
- Key Partners
- The structure of costs.
As you can see, this structure covers all the details of the enterprise’s activities, both inside the organization and with the external market.
If you want to think over the business model of your business, now you can take a pencil and start thinking through the answers for each block.
Block # 1. Customer segments – thinking over this block, the company must make a choice and decide which segments to serve, and which ones to refuse. Customers are the heart of any business model. It is with this and it is worth starting.
Here you need to answer the following questions:
- Who are you working for?
- Which clients are more important to you?
Answering these questions, you will see what segment of the market you are covering, it can be:
– mass market (a large group of consumers, which are united by similar needs and needs);
– niche market (special consumer segments);
– a market with fractional segmentation (several consumer segments with slightly different needs and requests);
– a diversified enterprise (such an organization serves two completely different consumer segments with different requests and needs);
– Multilateral platforms (these enterprises operate with two or more interconnected consumer segments).
Block # 2. Value propositions are a set of advantages that a company is ready to offer to a consumer. In this case, each value proposition must meet the requirements of a certain consumer segment. In order to qualitatively think over and describe the goods and services that are of value to your client, you need to think about the following:
- What values does your company offer to the customer / consumer?
- What problems of clients do you solve?
- What kind of goods and services can you offer to each consumer segment?
To correctly answer these questions, you must clearly understand the “pain” of your client. Based on the results of such a survey, you will get a list of problems and values. You can see that the requirements of the consumer can be not only as a product or service, but also in price, service speed, emotions experienced by the customer when buying, using, etc.
The value of a product or service consists of different elements, it can be either novelty, productivity or an individual approach, exclusivity.
Therefore, this question is much deeper than it seems at first glance. So, what are you selling?
Block # 3. Distribution channels. As you can see, the sequence of blocks is logical. Having chosen a segment of the market and having designated a value proposition, it is necessary to work out a sales channel. Here we mean, not only sales channels, but also channels for maintaining communication with consumers. Analyzing this block it is important to think over the effectiveness of each channel. In order to “sketch out” the list of channels of interaction with customers, you can answer such questions:
- What channels are convenient for your customers?
- How do you work with them now?
- How are your channels connected to each other?
- Which are the most effective?
- Which are more profitable?
It is important to think about the optimal balance between the various distribution channels and find a combination of these that will provide the best consumer feedback and maximum revenue.
Block # 4. Relationship with customers – the next block describes the types of relationships that are established with the company with individual customer customers. You may think this block is too “and so understandable” and maybe even you think that it is completely superfluous and it is not worth thinking about. However, let’s go deep and go “from the client”:
- What kind of relationship awaits each consumer segment from your company?
- What kind of relationship has been established?
- What are the costs of this relationship?
Here you can think a lot, because, in fact, today’s business is a relationship. And the way the company shows itself, has a significant impact on consumer behavior.
Decide whether your relationship with customers will be automated or personal. And then think over the options for interaction, perhaps it will be personal support or special personal support, the Internet community or even a joint creation.
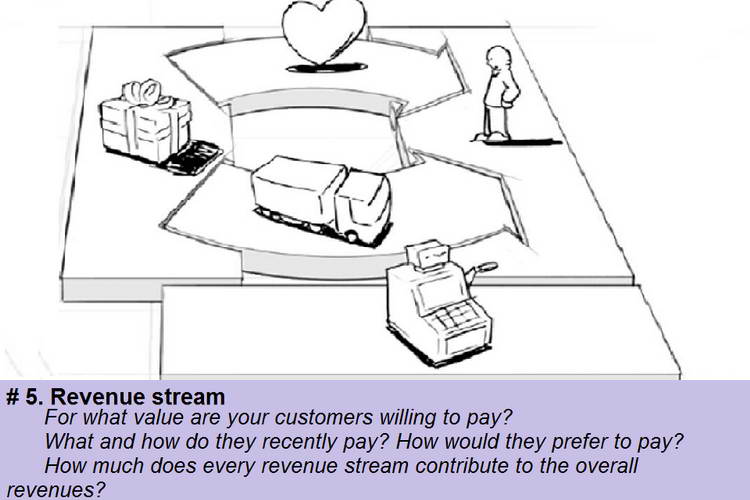
Block # 5. Revenue streams. This block will help answer all questions related to income receipts, price and type of cash flow. In the business model, there are two types of revenue stream: regular income from periodic payments, as well as income from one-off transactions. These types of flows depend on the pricing mechanism: fixed or contractual prices, auction trades, prices depending on the market or volume of sales, etc.
The best way to help you decide how and for what, your customers will pay – answers to such questions:
- What are customers really willing to pay for?
- What are they paying for now?
- How do they pay?
- How would they prefer to pay?
- What part of the total profit brings each income stream?
The revenue unit – has a hidden potential. Here you can vary with the mechanism of pricing and the type of values that the company sells. Thinking about this block, you can find additional sources of income that have not yet been used, for example: payment for use, subscription fees, renting something, surrendering rights to intellectual property, advertising, mediation.
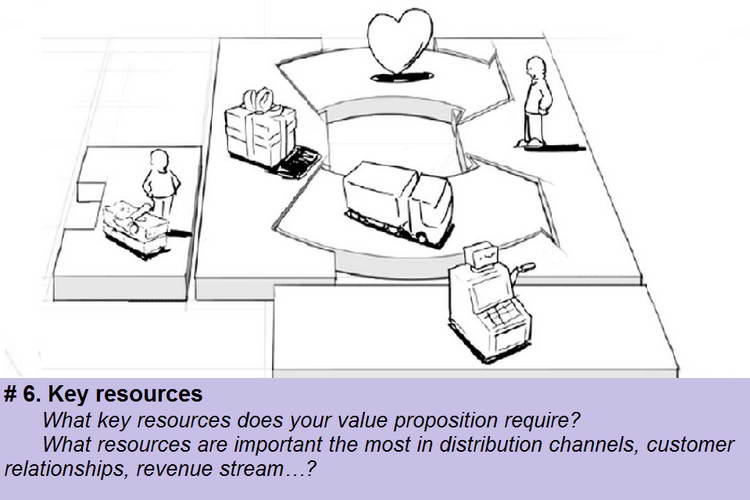
Block # 6. Key resources are resources that allow the company to create and communicate value propositions to consumers, enter the market, maintain connections with consumer segments and make profit. Different types of business models require different resources. At the same time, the company can be the owner of these resources, and can take them on lease, or on partner terms. To optimize key resources, answer these questions:
- What key resources are needed for your business?
- What are the key resources for the distribution channel?
- What key resources are needed for customer relationships?
- What key resources are needed to create revenue streams?
The main key resources of the company can be: material resources, intellectual resources, personnel, finance.
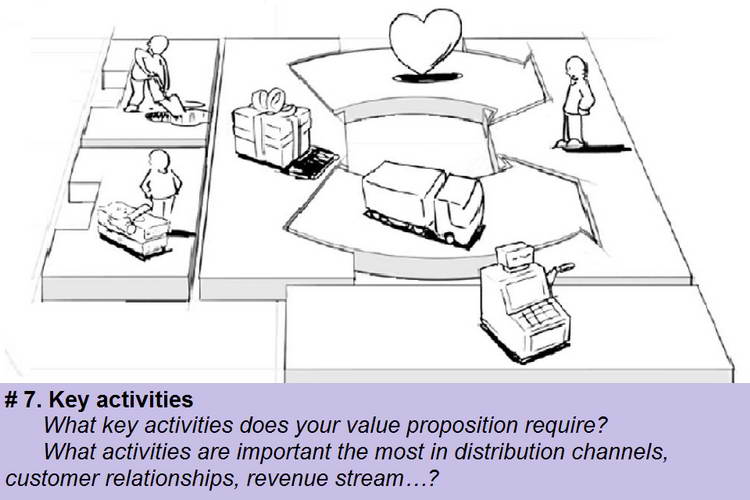
Block # 7. The key activities are the most important actions of the company, without which its successful work is impossible. Depending on the type of business model, the key activities of the company may be in the following areas:
– development, creation and launch of a product (production model);
– resolution of problems (business model requires knowledge management, continuous development of professional skills);
– platforms and networks (the main activity of this type is connected with the management of platforms, service provision and promotion of platforms).
In order to understand key activities, you can answer these questions:
- What actions are required for your service or product? \
- What are your sales channels?
- What are your relationships with customers?
- What are your revenue streams?
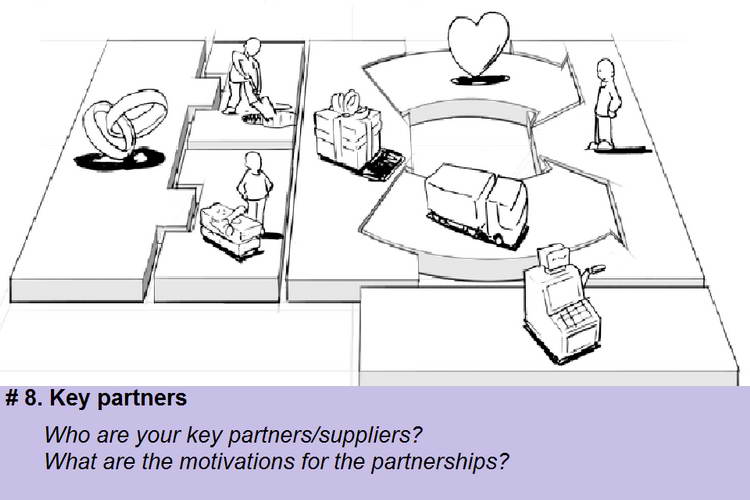
Block # 8. Key partners. This block is designed to think through the main partners and suppliers. Partnerships are created in order to optimize their business models, reduce risks or get resources. At the same time, different types of relations can be formed between partners. For effective work of your business it is necessary to think over this block and answer such questions:
- Who are your key partners?
- Who are your main suppliers?
- What are the key resources of your partners?
- What is the main activity of your partners?
However, the motives for creating partnerships can be different:
Optimization and economy in the sphere of production;
Risk reduction;
Supply of resources and joint activities.
Block # 9. Cost structure. The block gives an idea of the structure of costs associated with the functioning of the business model. The costs are fairly easy to calculate if you have accurately identified key resources, key activities and key partners. Minimize costs should be in any business model. When formulating the list of cost structures, you need to pay attention to:
What are the most important costs in your business model?
- What are the most expensive costs?
- What are the main activities that require the most costs?
So, after working through these 9 blocks before you will be – a template for the business model. Prepare yourself for the fact that this template will change more than once. Now that the sketch is before you, you can continue designing to the most optimal business model, for a given time with the available output data.
Innovations in Business Modeling
It should be noted that to think through your business model, you need not only analyze the activities of competitors and be based on already established traditions in this area, but it is best to ask yourself questions: “what if?”.
The process of innovation in business models has nothing to do with the past, because there you will not find any clues to what the future has prepared. Copying competitors – just will not give results, because the main task – is the creation of new values for the needs of consumers.
We urge you to be not only an informed entrepreneur and to forecast the situation ahead, but also want to awaken in you an innovative and creative approach to business.
In practice, the business model is a system in which each element affects all others; It only makes sense as a whole. Therefore, it is important to create a visual image of your model, visualizing the work of your business will give you a fresh look at the hardened foundations. You will definitely see hidden opportunities, unused connections, open logical inconsistencies.
The process of developing a business model is like a mathematical problem, in which the solution is not only the largest profit measure, but also the ability to scale and flexibility.
Why do you need all this? In order for you to realize that there is not one single right business model. In fact, there are a lot of opportunities and options that are suitable for this time in this particular place and just for you.
Decide, plan and you will understand that planning is not a setting of constraints, but a search for opportunities.